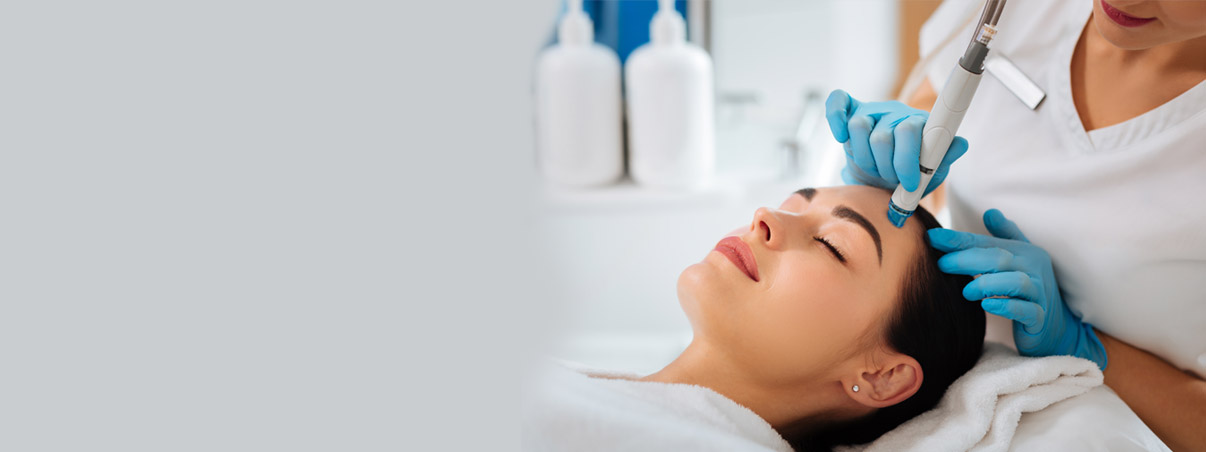
Hormonal Imbalance: One of the primary reasons for excessive facial hair in women is hormonal imbalance. Hormones like testosterone, typically associated with males, are also present in smaller quantities in females. When these hormonal levels become imbalanced, it can lead to an increase in facial hair growth. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and adrenal gland disorders can contribute to this hormonal disruption.
Genetics: Genetics plays a significant role in determining the extent of facial hair in women. If your family has a history of hirsutism (excessive hair growth), you are more likely to experience it yourself. Certain ethnic backgrounds also have a higher predisposition to facial hair.
Medications: Some medications, such as steroids and certain contraceptives, can stimulate hair growth in unwanted areas, including the face. If you suspect your medication is contributing to facial hair growth, consult your healthcare provider for alternative options.
Idiopathic Hirsutism: In some cases, the exact cause of excessive facial hair in women remains unknown. This condition is referred to as idiopathic hirsutism and may require a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional.
Age: As women age, their hormone levels fluctuate, and this can affect facial hair growth. It is common for some women to experience an increase in facial hair as they approach menopause.
Medical Conditions: Underlying medical conditions, such as Cushing's syndrome and congenital adrenal hyperplasia, can lead to abnormal hair growth in women. Identifying and treating these conditions is crucial to managing excessive facial hair.